Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
Take the first step to better health with Dr. Chowdhury, our highly experienced Foot & Ankle Surgeon!
Request Appointment

Overview
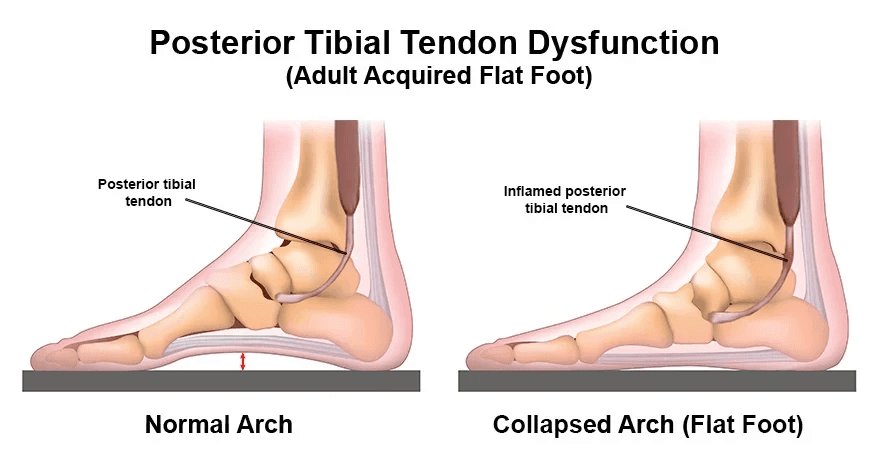
PTTD, also referred to as posterior tibial tendonitis or posterior tibial tendon insufficiency, involves the gradual deterioration of the posterior tibial tendon. This tendon plays a crucial role in supporting the foot arch by connecting the calf muscle to the bones along the inner side of the foot. When damaged or weakened, it can result in the flattening of the foot arch, accompanied by intense pain in the foot and ankle. The condition's degenerative nature may restrict range of motion and affect balance and mobility, making activities like walking and running challenging.
Request Appointment
Struggling With Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction?
Symptoms
Symptoms of PTTD vary in severity but often include pain and swelling along the inner side of the foot and ankle, particularly exacerbated during activity. Patients may experience limited mobility, inward rolling of the ankle, flattening of the foot arch, and difficulty standing or walking. In advanced stages, arthritis may develop, further complicating the condition.
Risk Factors
PTTD primarily affects individuals over 40, particularly those engaged in high-impact sports. Risk factors include obesity, hypertension, diabetes, previous foot or ankle injuries, joint disorders, steroid use, and overuse of the ankle joint, such as in long-distance running or basketball.
Diagnosis
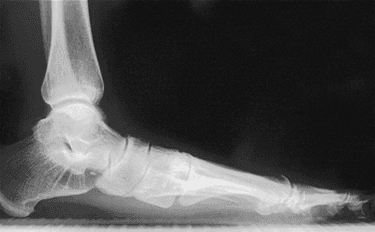
The diagnostic process for PTTD typically involves a thorough physical examination, including a detailed medical history and observation of movement patterns. Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, CT scans, or ultrasound may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis.
Visual Indicators
Characteristic visual signs of PTTD include inward rolling of the ankle, collapse of the foot arch, and outward pointing of the toes as the posterior tibial tendon continues to degenerate. Additionally, patients may exhibit a worsening limp.
Treatment
Treatment for PTTD varies based on severity but may initially involve non-surgical approaches like customized orthotics, shockwave therapy, immobilization, rest, ice, medications, physical therapy, and bracing. If non-surgical methods fail to yield improvement, surgical options, including posterior tibial tendon reconstruction, may be considered.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Rest is crucial in managing PTTD, and high-impact activities should be avoided.
- Without treatment, PTTD will worsen over time, emphasizing the importance of proactive intervention.
- Recovery time depends on the severity of the condition and response to treatment, with surgical recovery typically involving a period of immobilization followed by rehabilitation.


Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
Take the first step to better health with Dr. Chowdhury, our highly experienced Foot & Ankle Surgeon!
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
Take the first step to better health with Dr. Chowdhury, our highly experienced Foot & Ankle Surgeon!


Overview
PTTD, also referred to as posterior tibial tendonitis or posterior tibial tendon insufficiency, involves the gradual deterioration of the posterior tibial tendon. This tendon plays a crucial role in supporting the foot arch by connecting the calf muscle to the bones along the inner side of the foot. When damaged or weakened, it can result in the flattening of the foot arch, accompanied by intense pain in the foot and ankle. The condition's degenerative nature may restrict range of motion and affect balance and mobility, making activities like walking and running challenging.
Symptoms
Symptoms of PTTD vary in severity but often include pain and swelling along the inner side of the foot and ankle, particularly exacerbated during activity. Patients may experience limited mobility, inward rolling of the ankle, flattening of the foot arch, and difficulty standing or walking. In advanced stages, arthritis may develop, further complicating the condition.
Visual Indicators
Characteristic visual signs of PTTD include inward rolling of the ankle, collapse of the foot arch, and outward pointing of the toes as the posterior tibial tendon continues to degenerate. Additionally, patients may exhibit a worsening limp.
Risk Factors
PTTD primarily affects individuals over 40, particularly those engaged in high-impact sports. Risk factors include obesity, hypertension, diabetes, previous foot or ankle injuries, joint disorders, steroid use, and overuse of the ankle joint, such as in long-distance running or basketball.
Diagnosis
The diagnostic process for PTTD typically involves a thorough physical examination, including a detailed medical history and observation of movement patterns. Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, CT scans, or ultrasound may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment for PTTD varies based on severity but may initially involve non-surgical approaches like customized orthotics, shockwave therapy, immobilization, rest, ice, medications, physical therapy, and bracing. If non-surgical methods fail to yield improvement, surgical options, including posterior tibial tendon reconstruction, may be considered.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Rest is crucial in managing PTTD, and high-impact activities should be avoided.
- Without treatment, PTTD will worsen over time, emphasizing the importance of proactive intervention.
- Recovery time depends on the severity of the condition and response to treatment, with surgical recovery typically involving a period of immobilization followed by rehabilitation.




Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
Take the first step to better health with Dr. Chowdhury, our highly experienced Foot & Ankle Surgeon!
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
Take the first step to better health with Dr. Chowdhury, our highly experienced Foot & Ankle Surgeon!


SPORTS FOOT &
ANKLE CENTER
Services
Achilles Tendonitis
Ankle Fracture
Lisfranc Injury
Ankle Sprain
... + 20 more
Reviews
Jessica Peri
Sameer Alam
Noman Saleemi
Andres Botero
…+ 6 more
Contact
201-777-1245
dr.einfootandankle@gmail.com
Location
SPORTS FOOT &
ANKLE CENTER
Services
Achilles Tendonitis
Ankle Fracture
Lisfranc Injury
Ankle Sprain
... + 20 more
Reviews
Jessica Peri
Sameer Alam
Noman Saleemi
Andres Botero
…+ 6 more
Location
Contact
201-777-1245
dr.einfootandankle@gmail.com


Request Appointment
Struggling With Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction?
SPORTS FOOT &
ANKLE CENTER
Services
Achilles Tendonitis
Ankle Fracture
Lisfranc Injury
Ankle Sprain
... + 20 more
Testimonials
Jessica Peri
Sameer Alam
Noman Saleemi
Andres Botero
…+ 6 more
Location
Contact
201-777-1245
dr.einfootandankle
@gmail.com




Overview
PTTD, also referred to as posterior tibial tendonitis or posterior tibial tendon insufficiency, involves the gradual deterioration of the posterior tibial tendon. This tendon plays a crucial role in supporting the foot arch by connecting the calf muscle to the bones along the inner side of the foot. When damaged or weakened, it can result in the flattening of the foot arch, accompanied by intense pain in the foot and ankle. The condition's degenerative nature may restrict range of motion and affect balance and mobility, making activities like walking and running challenging.
Visual Indicators
Characteristic visual signs of PTTD include inward rolling of the ankle, collapse of the foot arch, and outward pointing of the toes as the posterior tibial tendon continues to degenerate. Additionally, patients may exhibit a worsening limp.
Symptoms
Symptoms of PTTD vary in severity but often include pain and swelling along the inner side of the foot and ankle, particularly exacerbated during activity. Patients may experience limited mobility, inward rolling of the ankle, flattening of the foot arch, and difficulty standing or walking. In advanced stages, arthritis may develop, further complicating the condition.
Risk Factors
PTTD primarily affects individuals over 40, particularly those engaged in high-impact sports. Risk factors include obesity, hypertension, diabetes, previous foot or ankle injuries, joint disorders, steroid use, and overuse of the ankle joint, such as in long-distance running or basketball.
Diagnosis
The diagnostic process for PTTD typically involves a thorough physical examination, including a detailed medical history and observation of movement patterns. Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, CT scans, or ultrasound may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment for PTTD varies based on severity but may initially involve non-surgical approaches like customized orthotics, shockwave therapy, immobilization, rest, ice, medications, physical therapy, and bracing. If non-surgical methods fail to yield improvement, surgical options, including posterior tibial tendon reconstruction, may be considered.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Rest is crucial in managing PTTD, and high-impact activities should be avoided.
- Without treatment, PTTD will worsen over time, emphasizing the importance of proactive intervention.
- Recovery time depends on the severity of the condition and response to treatment, with surgical recovery typically involving a period of immobilization followed by rehabilitation.